Graph in Python
Constructor
The Graph class constructor should take in:
- nvertices: the number of vertices, defaults to
0 - edges: a
defaultdict(set)mapping a vertex (start: int) to set of vertices ({int}), indicating there is an edge from start to each vertex in the set. - directed: a boolean, defaults to
False - weights: a dictionary mapping edges
(Vertex, Vertex)to integers (int).
If the number of vertices is not specified, the constructor should
call a helper function update_nvertices() to deduce the number of vertices from the
adjacency list of edges.
Directed Graphs
When directed is True, no changes are made to the provided edges.
When directed is False, the constructor should call a helper function
update_undirected_edges() that ensures every edge is
bidirectional. (Be careful if modifying a list while iterating through
the same list.) This is a convience for humans, so we do not have to
type both directions of an edge.
String representation
The graph should print out as:
"[Graph, V={number of vertices}, E={edge list}, W={weights}]"
Graph from a File
A graph is represented in a file of this form:
# Comments start with the pound sign
SOURCE_VERTEX TARGET_1 TARGET_2 ... # adjacency list rep
...
# WEIGHTS
START END WEIGHT
The “weights” section is optional. It follows the special comment “# WEIGHTS”.
The Graph class has a static method called from_file.
def from_file(openfile, directed):
return Graph()
The inputs are:
cls, the class, which is going to beGraphopenfile, a TextIO object, which acts just like an open filedirected, a boolean which defaults toFalse
Usage:
with open("GraphK33.txt") as f:
v = Graph.from_file(f, directed=False)
In general, you should remove comments (possibly following the in-class discussion; a regular expression is fine) and skip blank lines.
Example 1: a triangle.
0 1 2
1 2
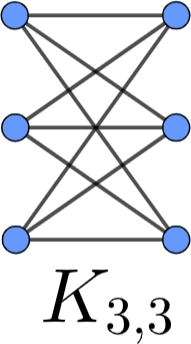
Example 2: the graph known as $K_{3,3}$.
# K_{3,3}
11 21 22 23
12 21 22 23
13 21 22 23
Advanced Features
- Write a
cleanup()function that renumbers the vertices to be consecutive integers beginning with 0.
Graph from a String
A class method `from_str’ converts a (multiline) string into a Graph.
@classmethod
def from_str(cls, txt, directed=False):
return Graph()
This method is very short because you can use StringIO to treat a string like a file.
Example:
triangle_oneway = Graph.from_str('''
0 1 2
1 2
''', directed=True)